- What does BYD stand for?
- Who is BYD?
- When was it founded and by whom?
- What was BYD’s original business before making cars?
- When did the brand start producing automobiles? What was their first car model?
- What models are on offer in the UK?
- How has BYD’s model range and production capacity grown over time?
- When did the brand first expand internationally? What markets are they in now?
- Who are the key leaders and executives that have shaped BYD’s strategy?
- What breakthroughs has BYD made in EV and battery technology?
- How has BYD’s reputation for build quality changed over time?
- What is BYD’s long-term vision looking forward?
- How does BYD’s growth and success compare to other major Chinese auto brands?
- What challenges has BYD faced and how have they responded?
What does BYD stand for?
BYD stands for “Build Your Dreams”. This optimistic company name represents BYD’s vision to create forward-thinking electric vehicle technology that helps build a more sustainable future.
Who is BYD?
BYD (Build Your Dreams) is an automotive company based in Shenzhen, China that manufactures affordable electric vehicles.
Founded in 1995, the company has grown from a humble battery business into one of the largest EV makers globally, selling over 1.5 million electric vehicles worldwide so far.
When was BYD founded and by whom?
The Chinese car manufacturer was founded in February 1995 by Wang Chuanfu, a Chinese chemist and government researcher.
Based in Shenzhen, Wang started the company as a rechargeable battery company producing Li-ion and NiCd batteries for mobile devices.
He contributed his knowledge of metallurgy and material sciences to develop better battery technology.
What was BYD’s original business before making cars?
For its first eight years, BYD focused solely on rechargeable batteries, not automobiles. The company supplied batteries to major mobile device makers including Nokia, Motorola, and Samsung.
They became China’s largest battery supplier, helping fund their expansion into the car business.
When did BYD start producing automobiles? What was their first car model?
In 2003, BYD leveraged its expertise in batteries to begin developing electric vehicles. They purchased a Chinese state-owned car factory in 2003 and debuted their first petrol-powered saloon.
In 2008, the brand launched its first hybrid electric model – the F3DM compact saloon. This pioneering plug-in hybrid set the stage for BYD’s move into EVs.
What models does BYD offer in the UK?
Atto 3 – Compact electric SUV that just launched in 2022. BYD’s newest model for Europe offers a stylish design and generous standard equipment for the price. Comes with a 201 hp electric motor and up to 261 miles of range.

Dolphin – Launched in 2023, a midsize family-friendly EV with up to 265 miles of electric range and lively performance.
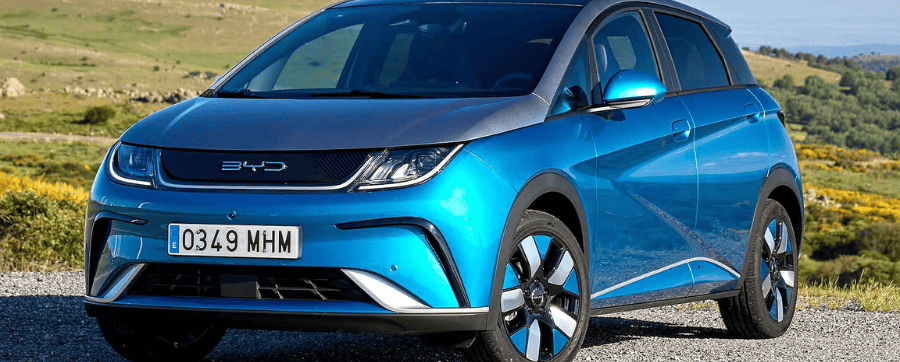
Seal – A fully electric saloon that was the third new car from the Chinese manufacturer to launch in 2023, this model comes in two forms – rear and all-wheel drive. Drivers can enjoy up to 354 miles of range.
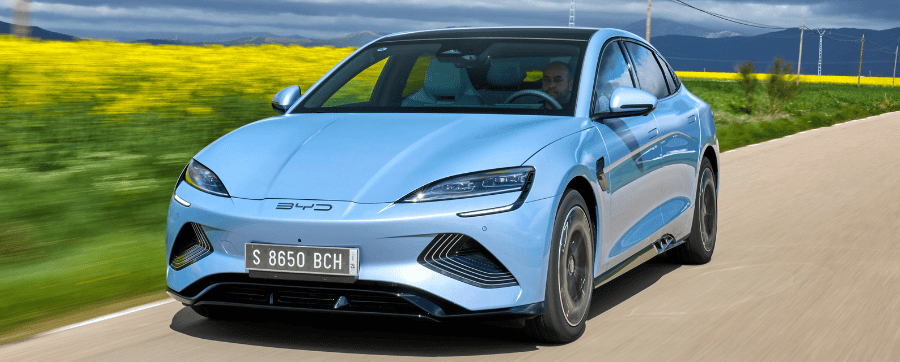
That covers the current and upcoming offerings in the UK market. The newest Atto 3 and Dolphin are the most affordable yet compelling options from BYD.
How has BYD’s model range and production capacity grown over time?
From just a few test models in the 2000s, the manufacturer now produces a wide array of EVs including saloons, SUVs, MPVs, buses, vans, and more. They operate 8 car factories in China producing over 1 million cars annually.
Recent models like the Atto 3, Dolphin, and Seal demonstrate how the company has expanded into appealing designs.
When did BYD first expand internationally? What markets are they in now?
The Chinese car manufacturer made its first international expansion in 2008, entering the US market. Today they have a presence in over 50 countries in Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Africa.
Key overseas markets include Norway, Netherlands, Japan, Colombia, India, and beyond. The company is accelerating global growth plans.

Who are the key leaders and executives that have shaped BYD’s strategy?
Chemist Wang Chuanfu remains BYD’s Chairman today, leading strategy. Additionally, senior VP Stella Li has driven BYD’s design evolution.
Young talent like Global VP Michael Shu are also guiding BYD’s future. This blend of veteran founders and new blood keeps the brand innovative.
What breakthroughs has BYD made in EV and battery technology?
BYD has pioneered advancements in lithium batteries, semiconductors, motors, and other core EV tech.
Examples include the Blade Battery’s space-saving cell arrangement, high-density motors, and bi-directional charging capabilities. Their expertise gives BYD an edge.
How has BYD’s reputation for build quality changed over time?
Early BYD models faced criticism for unrefined quality versus combustion engine rivals.
But Build quality has improved substantially on recent models like the Seal luxury saloon, earning praise from reviewers. While still not luxury-grade, BYD is matching mainstream brands in fit/finish.
What is BYD’s long-term vision looking forward?
BYD aims to lead the “Electrification Revolution” by driving EV adoption globally.
They plan to expand to new vehicle segments like pickups while enhancing high-tech capabilities. BYD also intends to grow energy storage/management offerings beyond just vehicles.
How does BYD’s growth and success compare to other major Chinese auto brands?
BYD is now the top-selling EV brand globally, ahead of competitors like SAIC and Geely. 500,000+ EV sales in 2022 put BYD far ahead of Chinese rivals.
They also bested major US and European automakers in EV volumes this year. BYD’s focused EV strategy has given it an advantage over its peers.
What challenges has BYD faced and how have they responded?
Limiting BYD is their lack of brand recognition outside China.
By boosting international marketing and distribution, partnering with established brands, and delivering quality affordable EVs, BYD aims to raise its overseas profile.
It’s an ongoing process but the innovative company is making strides.


